Robotic Perception and Manipulation of Deformable Linear Objects
Page Structure:
Vision-based Dataset Generation
Auto-generated Wires Dataset for Semantic Segmentation with Domain-Independence
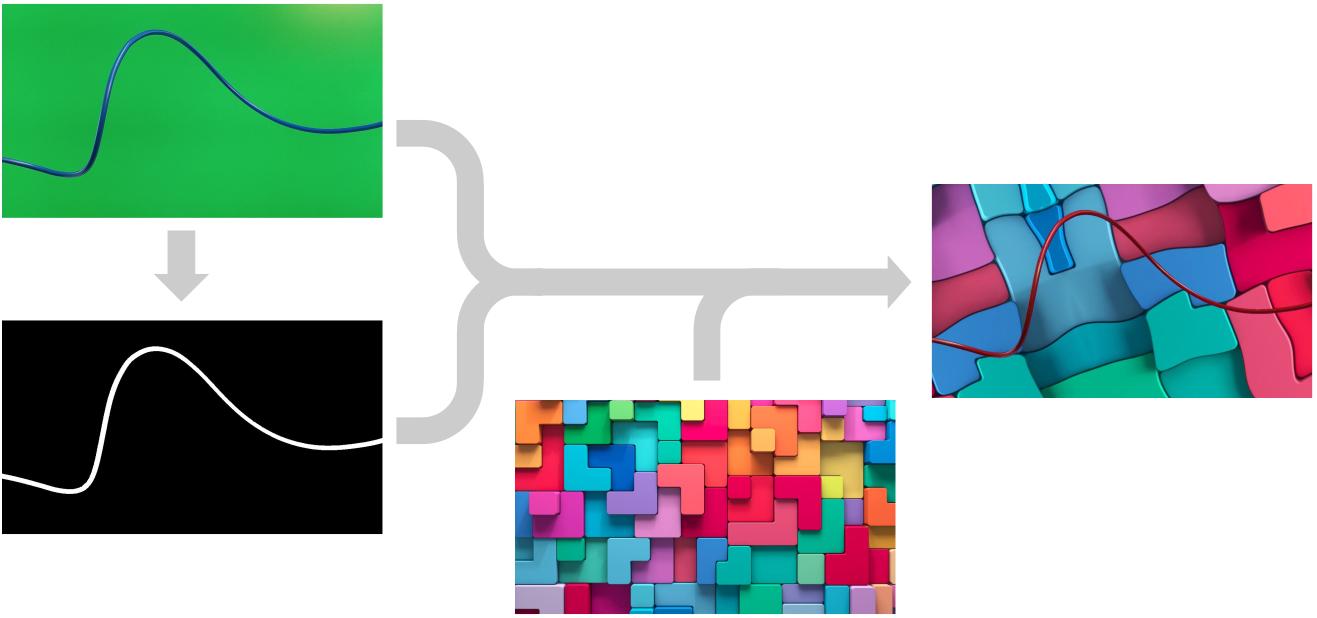
A procedure to automatically generate an high-quality training dataset of cable-like objects for semantic segmentation. The proposed method is explained in detail using the recognition of electric wires as a use case. These particular objects are commonly used in an extremely wide set of industrial applications, since they are of information and communication infrastructures, they are used in construction, industrial manufacturing and power distribution. The proposed approach uses an image of the target object placed in front of a monochromatic background. By employing the chroma-key technique, we can easily obtain the training masks of the target object and replace the background to produce a domain-independent dataset. How to reduce the reality gap is also investigated in this work by correctly choosing the backgrounds, augmenting the foreground images exploiting masks. The produced dataset is experimentally validated by training two algorithms and testing them on a real image set. Moreover, they are compared to a baseline algorithm specifically designed to recognise deformable linear objects. Paper / Dataset
A Weakly Supervised Semi-Automatic Image Labeling Approach for Deformable Linear Objects
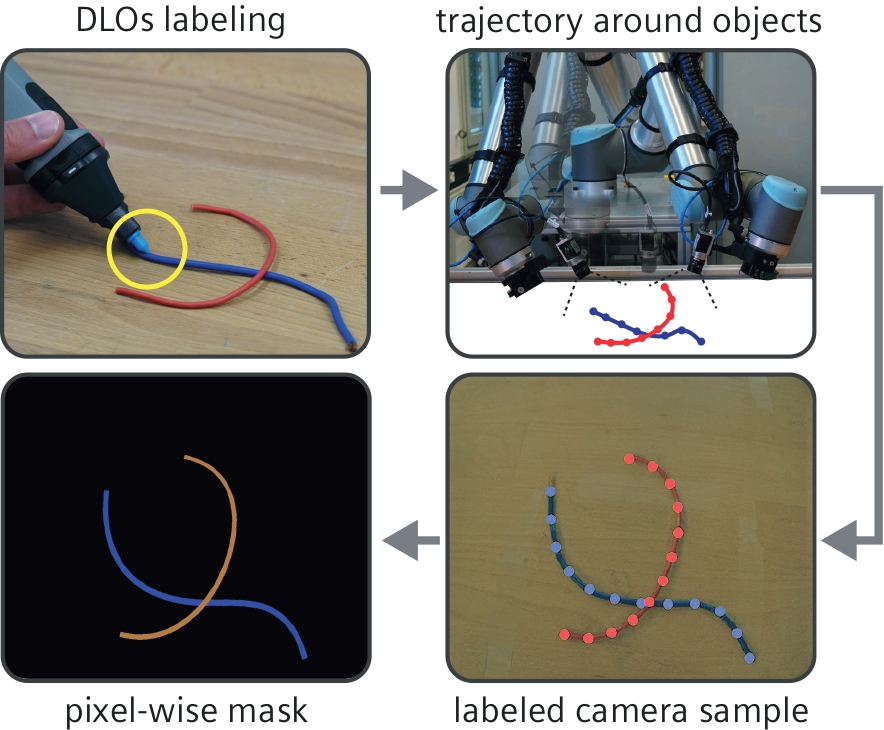
DLO-WSL: A methodology for generating datasets to train Deformable Linear Object (DLO) segmentation approaches involving combining synthetic and real samples. The process includes labeling key points on a real-world DLO using a VR tracker operated by a user. The datasets, comprising synthetic and real-world samples, are then used to train deep learning algorithms for semantic and instance segmentation. A user study and parameter analysis validate the method, demonstrating that VR tracker labeling is effective and reduces the number of clicks compared to alternative techniques. The results also indicate that blending real-world and synthetic DLO data enhances the Intersection over Union (IoU) score of a semantic segmentation algorithm by approximately 5%, highlighting the potential for improved segmentation algorithm performance when using a combination of real-world and synthetic data. Paper / Code / Video
2D Perception
Ariadne+ -- Deep Learning-Based Augmented Framework for the Instance Segmentation of Wires
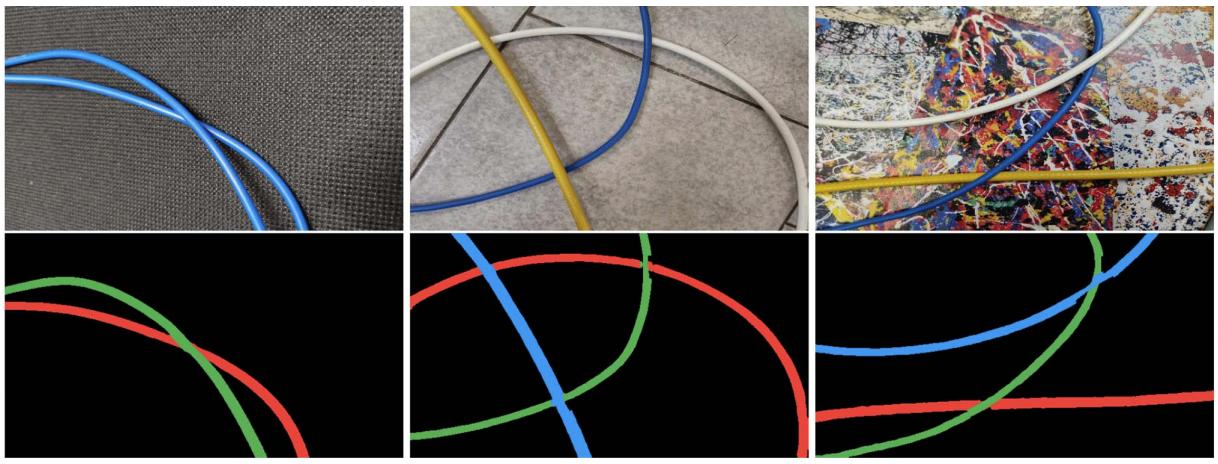
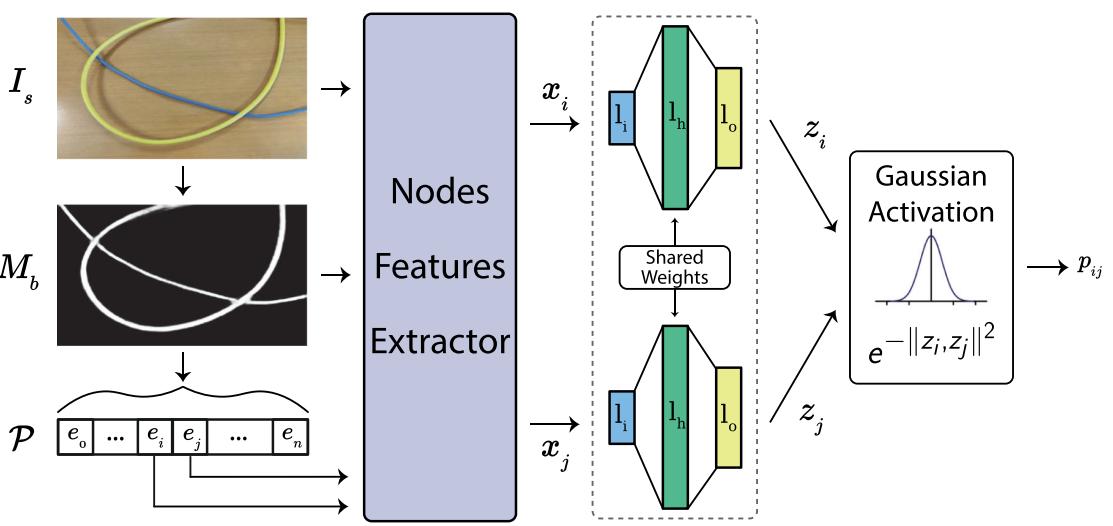
In this article, an innovative algorithm for instance segmentation of wires called Ariadne+ is presented. Although vastly present in many manufacturing environments, the perception and manipulation of wires is still an open problem for robotic applications. Wires are deformable linear objects lacking of any specific shape, color, and feature. The proposed approach uses deep learning and standard computer vision techniques aiming at their reliable and time effective instance segmentation. A deep convolutional neural network is employed to generate a binary mask showing where wires are present in the input image, then the graph theory is applied to create the wire paths from the binary mask through an iterative approach that aims to maximize the graph coverage. In addition, the B-Spline model of each instance, useful in manipulation tasks, is provided. The approach has been validated quantitatively and qualitatively using a manually labeled test dataset and by comparing it against the original Ariadne algorithm. The timings performances of the approach have been also analyzed in depth. Paper / Code
FASTDLO -- Fast Deformable Linear Objects Instance Segmentation
In this paper, an approach for fast and accurate segmentation of Deformable Linear Objects (DLOs) named FASTDLO is presented. A deep convolutional neural network is employed for background segmentation, generating a binary mask that isolates DLOs in the image. Thereafter, the obtained mask is processed with a skeletonization algorithm and the intersections between different DLOs are solved with a similarity-based network. Apart from the usual pixel-wise color-mapped image, FASTDLO also describes each DLO instance with a sequence of 2D coordinates, enabling the possibility of modeling the DLO instances with splines curves, for example. Synthetically generated data are exploited for the training of the data-driven methods, avoiding expensive collection and annotations of real data. FASTDLO is experimentally compared against both a DLO-specific approach and general-purpose deep learning instance segmentation models, achieving better overall performances and a processing rate higher than 20 FPS. Paper / Code
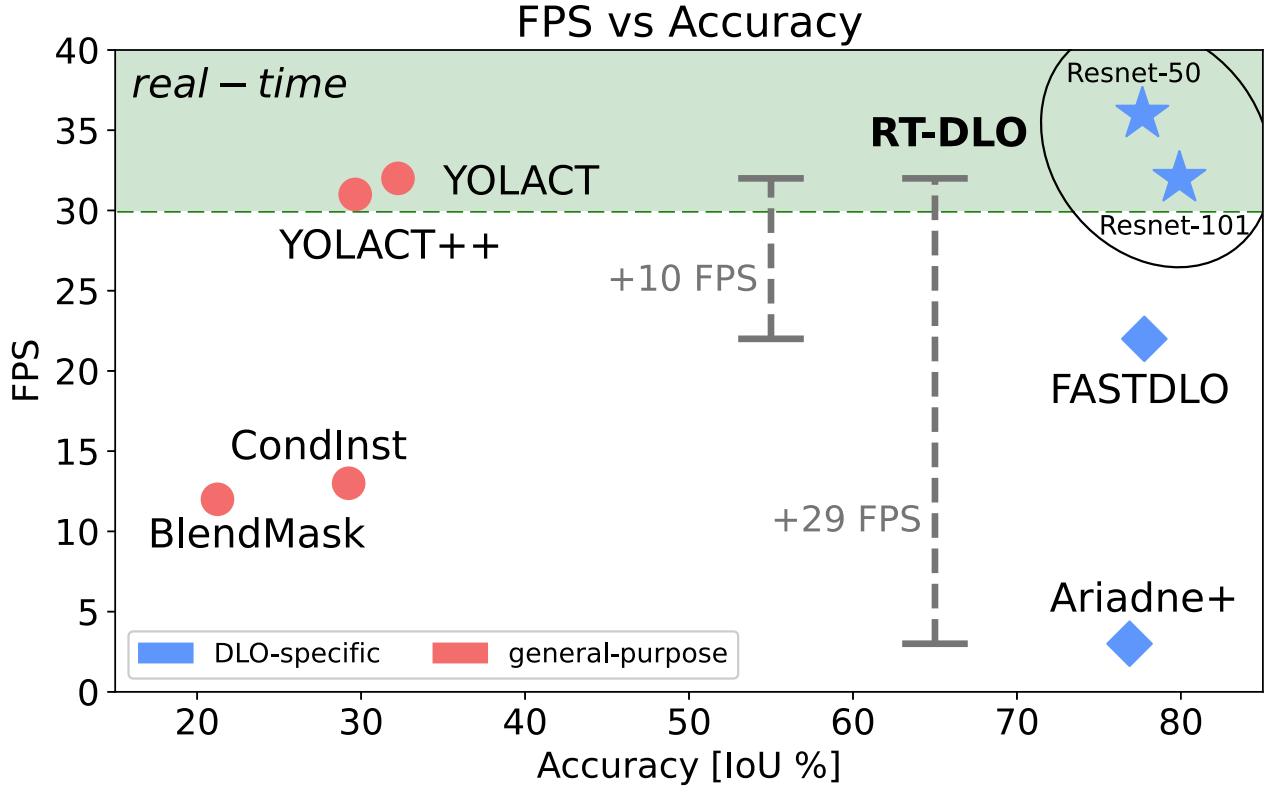
RT-DLO -- Real-Time Deformable Linear Objects Instance Segmentation
Deformable linear objects (DLOs), such as cables, wires, ropes, and elastic tubes, are numerously present both in domestic and industrial environments. Unfortunately, robotic systems handling DLOs are rare and have limited capabilities due to the challenging nature of perceiving them. Hence, we propose a novel approach named RT-DLO for real-time instance segmentation of DLOs. First, the DLOs are semantically segmented from the background. Afterward, a novel method to separate the DLO instances is applied. It employs the generation of a graph representation of the scene given the semantic mask where the graph nodes are sampled from the DLOs center-lines whereas the graph edges are selected based on topological reasoning. RT-DLO is experimentally evaluated against both DLO-specific and general-purpose instance segmentation deep learning approaches, achieving overall better performances in terms of accuracy and inference time. Paper / Code
3D Perception
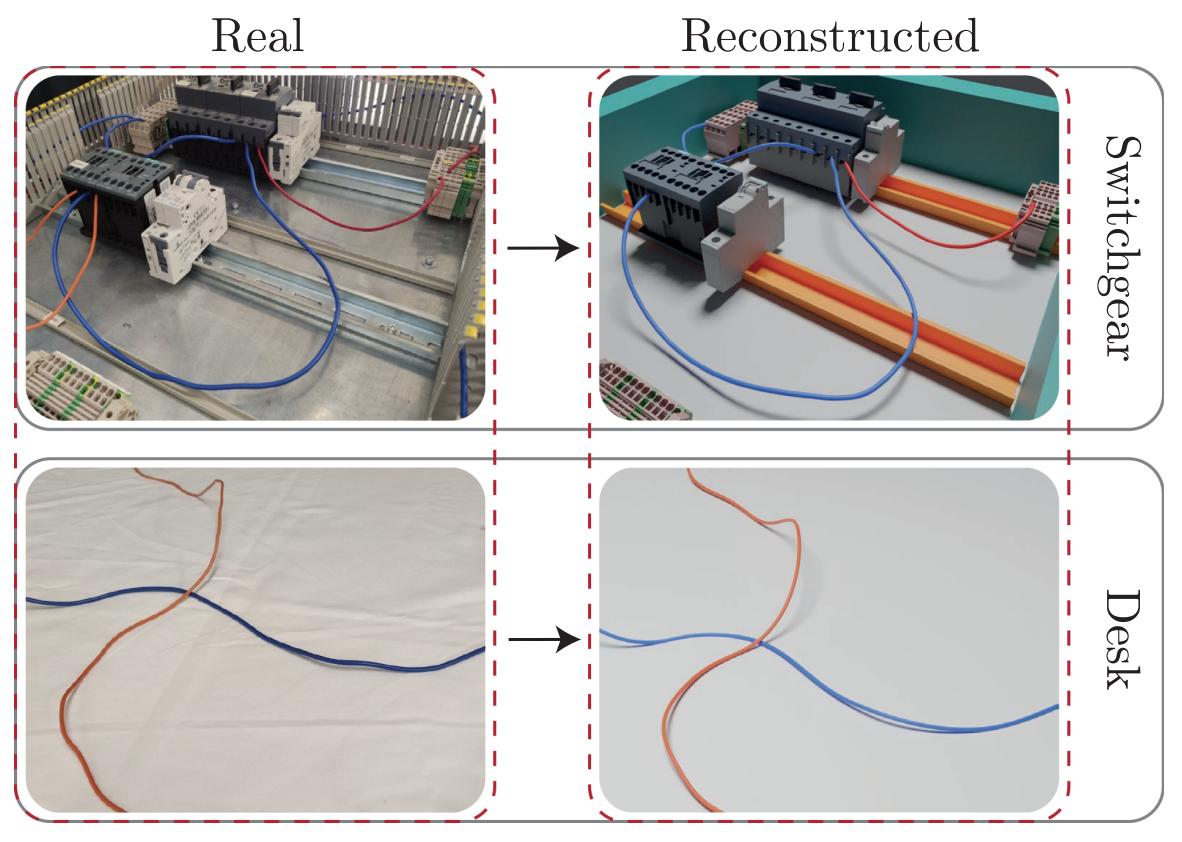
Deformable Linear Objects 3D Shape Estimation and Tracking From Multiple 2D Views
This letter presents DLO3DS , an approach for the 3D shapes estimation and tracking of Deformable Linear Objects (DLOs) such as cables, wires or plastic hoses, using a cheap and compact 2D vision sensor mounted on the robot end-effector. DLO3DS can be applied in all those scenarios in which the perception and manipulation of DLO-like structures are needed, such as in the case of switchgear cabling, wiring harness manufacturing and assembly in the automotive and aerospace industries, or production of hoses for medical applications. The developed procedure is based on a pipeline that first processes the images coming from the 2D camera extracting key topological points along the DLOs. These points are then used to model each DLO with a B-spline curve. Finally, the set of splines obtained from all the images is matched by exploiting a multi-view stereo-based algorithm. DLO3DS is validated both on a real scenario and on simulated data obtained by exploiting a rendering engine for photo-realistic images. In this way, reliable ground-truth data are retrieved and utilized for assessing the estimation error achievable by DLO3DS , which on the employed test set is characterized by a mean reconstruction error of 0.82 mm. Paper / Code
Manipulation
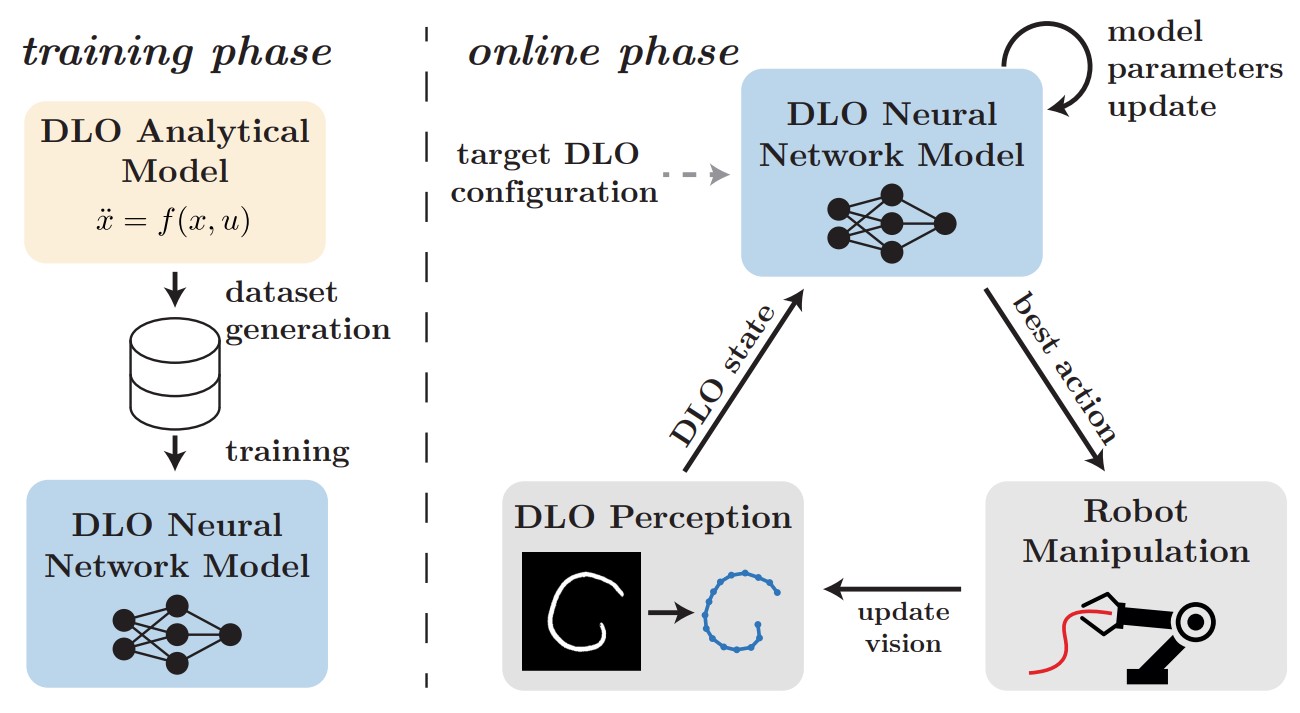
Deformable Linear Objects Manipulation with Online Model Parameters Estimation
Manipulating Deformable Linear Objects (DLOs) is a challenging task for a robotic system due to their unpredictable configuration, high-dimensional state space and complex nonlinear dynamics. This paper presents a framework addressing the manipulation of DLOs, specifically targeting the model-based shape control task with the simultaneous online gradient-based estimation of model parameters. In the proposed framework, a neural network is trained to mimic the DLO dynamics using the data generated with an analytical DLO model for a broad spectrum of its parameters. The neural network-based DLO model is conditioned on these parameters and employed in an online phase to perform the shape control task by estimating the optimal manipulative action through a gradient-based procedure. In parallel, gradient-based optimization is used to adapt the DLO model parameters to make the neural network-based model better capture the dynamics of the real-world DLO being manipulated and match the observed deformations. To assess its effectiveness, the framework is tested across a variety of DLOs, surfaces, and target shapes in a series of experiments. The results of these experiments demonstrate the validity and efficiency of the proposed methodology compared to existing methods. Paper / Code / Project_Website